|
|
|

|
|
314.420.5099 [Question Line] [back to Health Topics main page] /
[back to "A" main page] A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
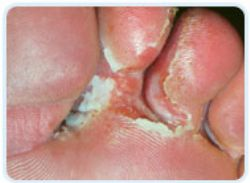
Athlete's foot is a skin disease caused by a fungus, usually occurring between the toes. Since this fungal condition was more common among athletes, the term athlete's foot became popular. Other areas of the body can be affected by this fungus, namely the groin or underarm areas. The fungus attacks the feet more often than other areas of the body because shoes create a warm, dark, and humid environment which a perfect atmosphere for fungal growth. The warmth and dampness of areas around swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms are also breeding grounds for fungi. Not all fungus conditions are athlete's foot. Other conditions, such as disturbances of the sweat mechanism, reaction to dyes or adhesives in shoes, eczema, and psoriasis, may mimic athlete's foot. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS The signs of athlete's foot, singly or combined, are dry skin, itching, scaling, inflammation, and blisters. Blisters often lead to cracking of the skin. When blisters break, small raw areas of tissue are exposed, causing pain and swelling. Itching and burning may increase as the infection spreads. Athlete's foot may spread to the soles of the feet and to the toenails. It can be spread to other parts of the body, notably the groin and underarms, by those who scratch the infection and then touch themselves elsewhere. The organisms causing athlete's foot may persist for long periods. Consequently, the infection may be spread by contaminated bed sheets or clothing to other parts of the body. PREVENTION It is not easy to prevent athlete's foot because it is usually contracted in dressing rooms, showers, and swimming pool locker rooms where bare feet come in contact with the fungus. However, you can do much to prevent infection by practicing good foot hygiene. Daily washing of the feet with soap and water; drying carefully, especially between the toes; and changing shoes and hose regularly to decrease moisture, help prevent the fungus from infecting the feet. Also helpful is daily use of a quality foot powder.
TREATMENT Often times, fungicidal and fungistatic chemicals that are used to treat athlete's foot will fail to contact the fungi in the horny layers of the skin. For this reason, topical or oral antifungal drugs are starting to become the prescription of choice. My favorite remedy of choice is grapefruit seed extract for athletes foot. I always recommended to my patients to take the grapefruit seed extract orally (capsule) and also as a topical directly on the affected area. The dosage should be what is recommended on the container. In mild cases of the infection it is important to keep the feet dry by dusting foot powder in shoes and hose. The feet should be bathed frequently and all areas around the toes dried thoroughly.
WHEN TO CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN If your apparent fungus condition does not respond to proper foot hygiene and self care, and there is no improvement within two weeks, consult your physician or podiatrist. The podiatrist will determine if a fungus is the cause of the problem. If it is, a specific treatment plan, including the prescription of antifungal medication, applied topically or taken by mouth, will usually be suggested. Such a treatment appears to provide better resolution of the problem, when the patient observes the course of treatment prescribed by the podiatrist; if it's shortened, failure of the treatment is common. If the infection is caused by bacteria, then antibiotics, such as penicillin, that are effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria may be prescribed by your physician. Naturally it is your choice whether you take the medical route or a more natural route.
/
[back to "A" main page]
[go to Supplements main page]
DISCLAIMER: **This web site's goal is to provide you with information that may be useful in attaining optimal health. Nothing in it is meant as a prescription or as medical advice. You should check with your physician before implementing any changes in your exercise or lifestyle habits, especially if you have physical problems or are taking medications of any kind. |
| 314.420.5099 |
| Questions regarding this site: webmaster@drstandley.com |
| Copyright 1999-2025: Dr. Loretta J. Standley - All Rights Reserved. |